Supercomputer Fugaku elucidates the infectivity of the novel coronavirus N501Y mutation strain
RIKEN (RIKEN) explained the progress of "Fragment molecular orbital calculation for novel coronavirus-related proteins" using the supercomputer "".
Fragment molecular orbital (FMO) calculations using ``'' to analyze in detail the ''complex'' between receptor-binding domain (RBD) mutants and angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) in human cells. . It is said that the N501Y mutation has revealed a change in the interaction mode that is directly related to infection, such as the enhancement of binding by the mutation.
Infection of the new coronavirus is caused by the interaction of RBD with ACE2, indicating that the charged residue plays an important role in structural changes and interactions, and is called 6M0J. Amino acid substitutions were made based on the wild strain, and molecular modeling software was used to show the RBD mutation sites.
Positional relationship near the interface of RBD-ACE2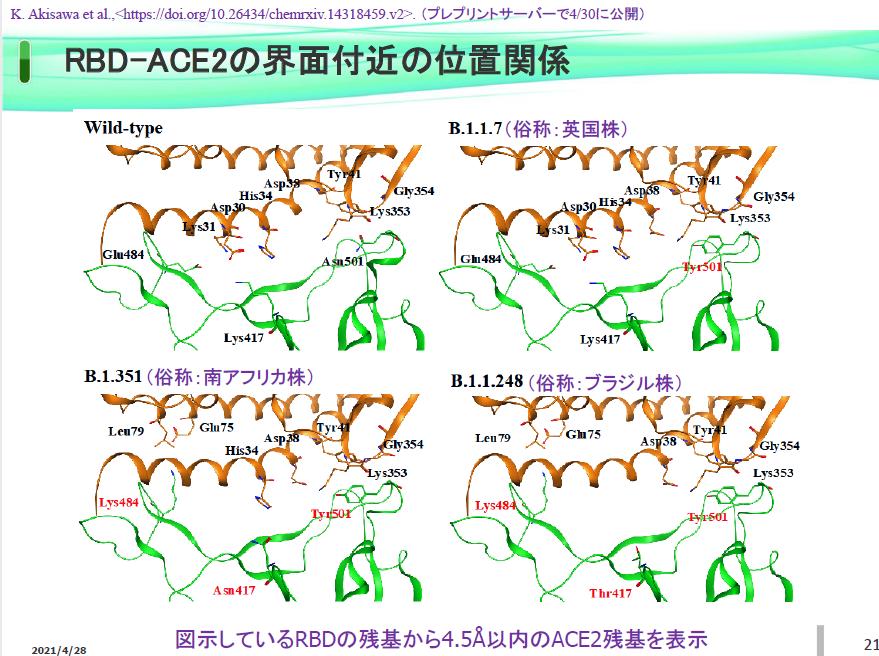
Professor Yuji Mochizuki of the Department of Chemistry, Faculty of Science, Rikkyo University, said, "Using the performance of , we were able to elucidate in detail the changes in the interaction and bond stabilization of the residue due to mutation. The increase in stabilization is We found that the N501Y mutation enhanced the binding of RBD and ACE2 in the vicinity of the contact surface, which is also evidence of increased infectivity. It matches," he said, adding, "We have demonstrated that FMO's computational chemistry research can help fight infectious diseases."
The N501Y mutation is also found in British, South African, and Brazilian strains, and infections are rapidly expanding in Japan. In N501Y, the 501st amino acid of the virus protein is mutated from asparagine (N) to tyrosine (Y). This makes it easier for the spike protein to bind to human cells, making it easier for the infection to spread.
In this study, we analyzed the dependence of the total interaction energy on the distance from the interface. It was found that the British stock (B.1.1.7 stock) has a relatively large stabilization of 1.05 times at a short distance from the interface. .248 shares (Brazilian stocks) have an advantage in stabilization, and the overall bond stabilization energy is 1.2 times higher.
Total interaction energy of RBD-ACE2 Dependence of distance from the interface of the sum of interaction energyWe also experimented with "coexisting models". According to Prof. Mochizuki, the results showed that the stability increased by 1.5 times due to the distance dependence.
In the future, we will analyze new mutant strains such as the Indian strain (B.1.617 strain) as needed.